Wei Zhenwei
Professor
Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
Supervisor of Master's Candidates
E-Mail:weizw2021@whu.edu.cn
Date of Employment:2021-02-01
School/Department:化学与分子科学学院
Administrative Position:教授
Education Level:With Certificate of Graduation for Doctorate Study
Business Address:化学与分子科学学院西南101
Gender:Male
Status:Employed
个人介绍
魏振威,男,汉族,武汉大学化学与分子科学学院教授,分析科学研究中心主任。2007-2016年就读于清华大学化学系,分别获得化学学士与博士学位(导师张新荣教授)。2016-2020于美国普渡大学化学系Aston Lab从事博士后研究工作,合作导师R Graham Cooks教授。2021加入武汉大学化学与分子科学学院,主要从事原位质谱分析方法学与仪器的研究。设计开发了直流诱导电喷雾、阶梯电压微电泳、诱导微电泳以及浮地电化学原位质谱分析等方法与仪器,成功用于单细胞代谢组组学、高通量反应筛查、原位电化学、光化学与微液滴化学反应监测与机理解析等研究,在Nat. Synth、Chem、JACS、ACIE、Anal. Chem.、Chem. Sci.等期刊上发表论文30余篇,参与编写质谱专著3部,2021年入选国家海外高层次人才计划,武汉市“武汉英才”计划。主持国家自然科学基金项目3项、科技部青年科学家仪器研发项目1项。现担任中国分析测试协会质谱分会与原子光谱分会委员,中国化学快报(英文版)青年编委。
课题组长期招聘博士后,欢迎各位同学来组内进行业余科研!欢迎感兴趣的同学积极联系报考本组研究生!
研究方向
本课题组主要致力于质谱分析方法学的研究,并以此为基础对于介观尺度下物理化学、生命科学以及合成科学的前沿问题进行研究,主要包括三个方向。
1.质谱离子化原理与质谱离子源
离子源是质谱的核心构成之一,发挥着将待测分子转化为带电离子并引入质谱的功能。我们致力于探究新颖的离子化原理和开发新型离子源以完成不同的分析任务。目前我们主要关注小体积样品(纳升至皮升级)的分析,重点发展样品损耗低的敞开式静电场诱导电喷雾方法以及电化学、光化学反应原位质谱分析方法等原位质谱分析技术。根据不同的实现原理与分析需求,通过3D打印制造零件搭建不同结构与功能的离子源装置;通过毛细管拉制仪与离子溅射装置,构筑不同分析需求中使用的纳升点喷雾载具;借助显微平台进行精细显微操作与微区分析。
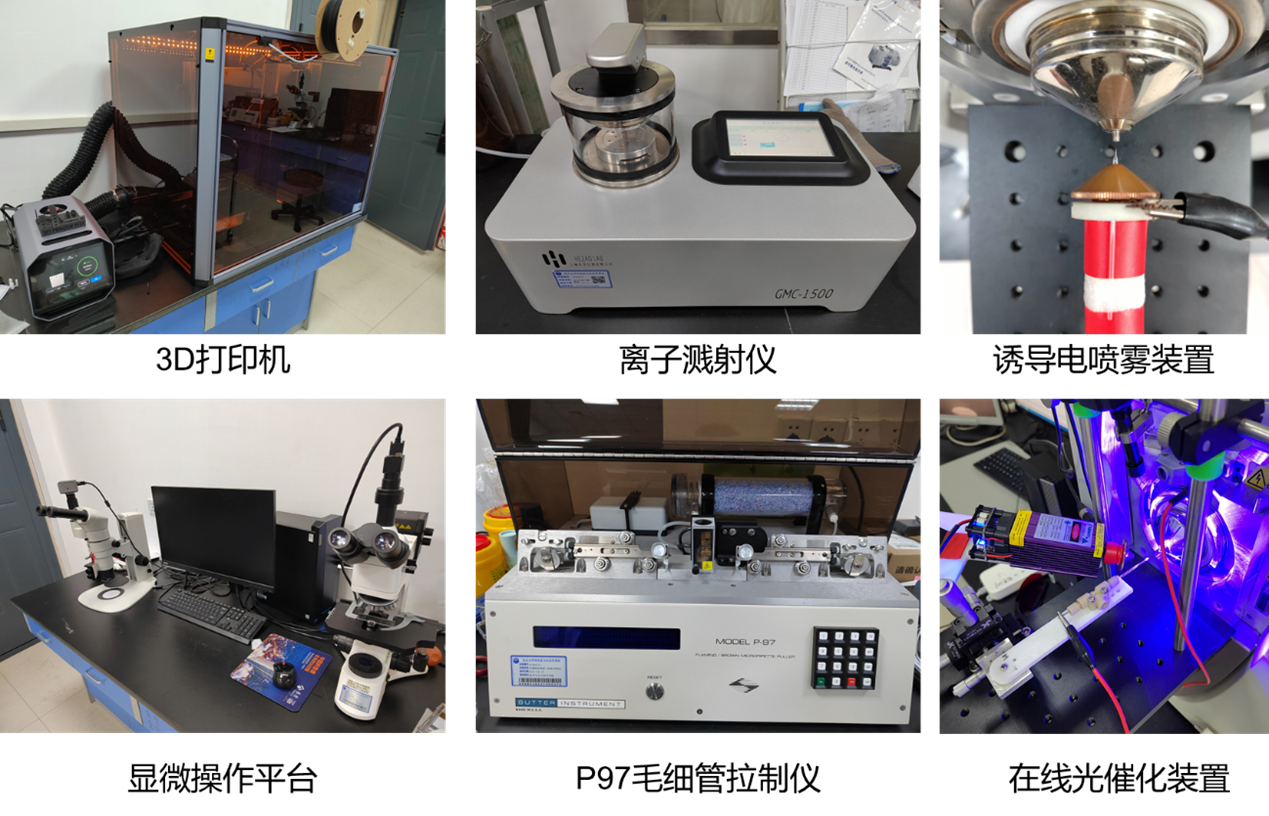

图1. 实验室离子源开发涉及的仪器与目前较为成熟的离子源分析系统
2.原位质谱反应监测方法
开发原位质谱离子化方法,对于化学反应过程进行监测具有重要意义。我们利用质谱对于气液界面的反应进行研究,发现微液滴比常规化学反应体系(试管烧瓶)中反应速率更快,转化率更高。事实上,这种独特的反应加速现象不仅存在于电喷雾中,还广泛存在于液体薄膜,囊泡等小体积空间内。我们关注微液滴反应加速的深层次机理,并且关注其在分析科学中的应用。
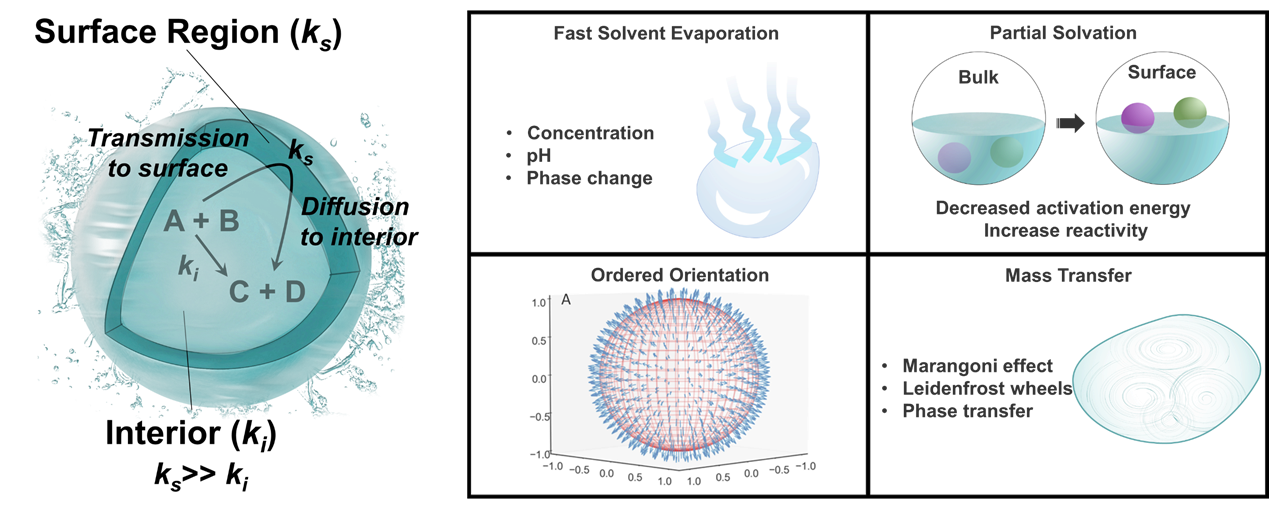
图2. 质谱反应监测技术探究微液滴化学反应机理
近年来,电化学催化与光化学催化在合成科学与分析科学中引起了广泛的研究兴趣。对活性中间体的表征可以为理解电化学反应的过程与机理提供重要的实验依据。我们基于敞开式离子化的设计思路,致力于开发新颖的、原位的、准确的电化学与光化学反应界面表征方法,例如电极/电解池与质谱离子源的集成化设计、界面产物的原位采样与离子化方法等。充分借助质谱法的高灵敏度和特异性,实现对于复杂电化学过程中间体的捕获、结构鉴定与定量分析,促进全新电化学反应机理的发现与验证。
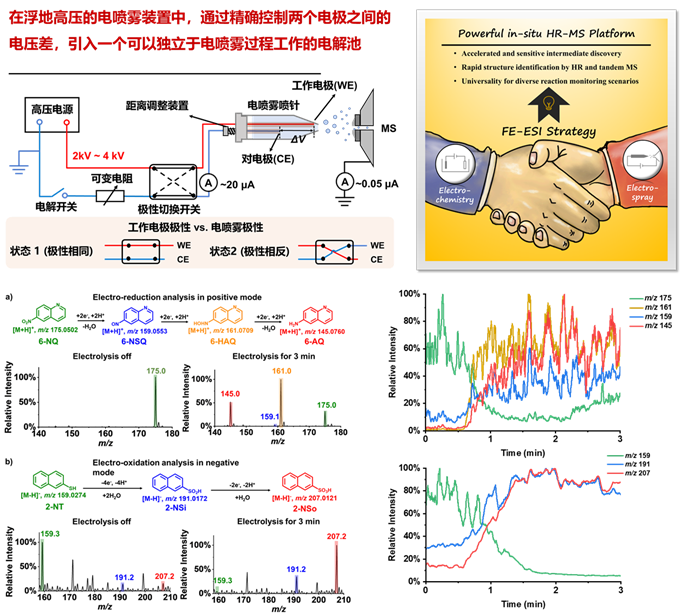
图3. 电位、电流精确可控电化学反应原位高分辨质谱分析系统,实现电化学反应中间体的定性与定量分析
3. 超小体积生物质谱分析方法
代谢物与蛋白质是生命活动的物质与能量基础,几乎参与了机体运行的所有过程。准确获得这些物质的结构、含量、时空信息对探索生命现象和解释生命活动规律具有重要意义。我们基于采样、富集、分离、检测一体化的设计思路,致力于开发快速的、原位的、微量的、高灵敏度的代谢物和蛋白质分析方法,例如单细胞及微区活体样本的质谱原位富集与分离方法、化学选择性标记-质谱亚代谢组分析方法、临床样本中大/小分子药物在线质谱分析方法等。通过将微分离、微萃取、微电泳、化学标记等前处理技术和质谱的创新式联用,实现对于小体积复杂生物样品中代谢物、蛋白质定性、定量和定位分析,促进对生命活动、疾病诊断与治疗等机制的新发现和新理解。
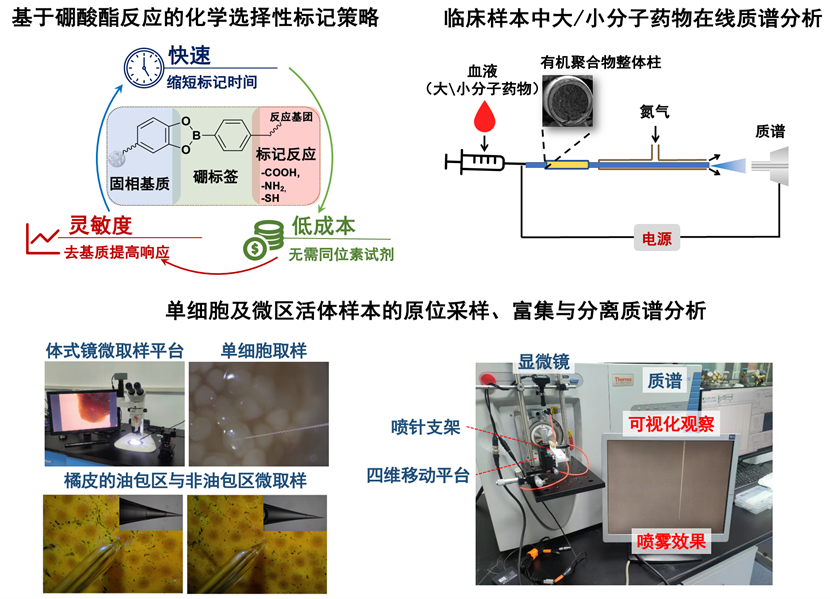
图4. 针对代谢物的微区分析、临床快检等需求开发的生物质谱分析方法与仪器装置
论文发表情况
[1] T. Zeng, Y. He, Y. Li, L. Wang, Q. Hu, Y. Li, Z. Wei, J. Chen, X. Qi, J. Zhu*. Photoredox cobalt-catalyzed asymmetric desymmetric reductive coupling of cyclobutenes with alkynes. Nat. Comm. 2025, 16, 3102.
[2] C. Zeng, J. Chen, C. Zhu, Z. Wei*. Highly sensitive and rapid screening of radical electrochemical intermediates by chemical labeling untargeted mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2025, 290, 127791.
[3] Y. Wang, J. Luo, Y.-G. Fang, Z.-A. Nan, X. Cui, T. Chen, X. Zeng, X. Wang, X. Song, J. Zhao, W. Li, C. Zeng, D. Chen, C. Zhu*, Z. Wei*, Z.-Q. Tian, F. R. Fan*. Catalyst-Free Nitrogen Fixation by Microdroplets through a Radical-Mediated Disproportionation Mechanism under Ambient Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 2756-2765.
[4] B. Xu, Y. Li, Z. Wei*. Familiarize Students with Direct MS Analysis Methods: Localization of Components in Citrus Peel by Induced Electrospray Ionization. J. Chem. Educ. 2024, 101, 2429-2435.
[5] W. Wang, J. Han, Y. Zheng, H. Wang, C. Zhu, Y. Li, Y. Feng, Z. Wei*, X. Wang*. Direct Analysis of Whole Blood by a Disposable Monolithic Column Mass Spectrometry Analysis Kit. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 1073-1078.
[6] X. Liu, J. Chen, Z. Wei*, H. Yi*, A. Lei*. Deciphering reactive intermediates in electrooxidative coupling of indoles through real-time mass spectrometry. Chem. 2024, 10, 2131-2146.
[7] Y. Li, J. Han, X. Wang, Z. Wei*. In-situ reaction monitoring and kinetics study of photochemical reactions by optical focusing inductive electrospray mass spectrometry. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 110708.
[8] J. Dong, J. Chen, W. Wang, Z. Wei*, Z.-Q. Tian, F. R. Fan*. Charged Microdroplets as Microelectrochemical Cells for CO2 Reduction and C-C Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2227-2236.
[9] X. Cui, J. Chen, H. Yi, Z. Wei*. Mapping Reaction Pathways by In Situ Step Sweep Voltammetry Flow Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 17765-17772.
[10] J. Han, X. Wang, W. Wang, J. Chen, B. Xu, Z. Wei*. Direct Analysis of Micro-biopsy Samples by Polarity Gradient Focusing Dip-and-Go Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13266-13272.
[11] J. Chen, X. Wang, X. Cui, Y. Li, Y. Feng, Z. Wei*. In Situ Probing and Identification of Electrochemical Reaction Intermediates by Floating Electrolytic Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202219302.
[12] X. Wang, P. Bai, Z. Li, Q.-F. Zhu, Z. Wei*, Y.-Q. Feng*. Rapid and Economical Chemoselective Metabolomics Using Boronate Ester Formation on a Monolithic Substrate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208138.
[13] X. Chen, Z. Wei, K.-H. Huang, M. Uehling, M. Wleklinski, S. Krska, A. A. Makarov, T. Nowak, R. G. Cooks*. Pd Reaction Intermediates in Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling Characterized by Mass Spectrometry. Chempluschem. 2022, 87, e202100545.
[14] Y.-L. Bai, X. Yin, C.-F. Xiong, B.-D. Cai, Y. Wu, X.-Y. Zhang, Z. Wei, T. Ye, Y.-Q. Feng*. Neophaseic acid catabolism in the 9'-hydroxylation pathway of abscisic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100340.
[15] L. Qiu, Z. Wei, H. Nie, R. G. Cooks*. Reaction Acceleration Promoted by Partial Solvation at the Gas/Solution Interface. Chempluschem. 2021, 86, 1362-1365.
[16] Y. Li, T. F. Mehari, Z. Wei, Y. Liu, R. G. Cooks*. Reaction acceleration at air-solution interfaces: Anisotropic rate constants for Katritzky transamination. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4585.
[17] Y. Li, T. Mehari, Z. Wei, Y. Liu, R. G. Cooks*. Reaction Acceleration at Solid/Solution Interfaces: Katritzky Reaction Catalyzed by Glass Particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2929-2933.
[18] K.-H. Huang, Z. Wei, R. G. Cooks*. Accelerated reactions of amines with carbon dioxide driven by superacid at the microdroplet interface. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 2242-2250.
[19] R. Chen, Z. Wei*, R. G. Cooks*. Collection and Characterization by Mass Spectrometry of the Neutral Serine Octamer Generated upon Sublimation. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1092-1099.
[20] Z. Wei, X. Zhang, X. Si, X. Gong, S. Zhang, X. Zhang*. Development of Pico-ESI-MS for Single-Cell Metabolomics Analysis. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.). 2020, 2064, 31-59.
[21] Z. Wei, Y. Li, R. G. Cooks*, X. Yan*, in Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, Vol 71, Vol. 71 (Eds.: M. A. Johnson, T. J. Martinez), 2020, pp. 31-51.
[22] H. Nie#, Z. Wei#, L. Qiu, X. Chen, D. T. Holden, R. G. Cooks*. High-yield gram-scale organic synthesis using accelerated microdroplet/thin film reactions with solvent recycling. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2356-2361.
[23] Z. Wei, Z. Xie, R. Kuvelkar, V. Shah, K. Bateman, D. G. McLaren, R. G. Cooks*. High-Throughput Bioassays using "Dip-and-Go" Multiplexed Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17594-17598.
[24] P. W. Fedick, K. Iyer, Z. Wei, L. Avramova, G. O. Capek, R. G. Cooks*. Screening of the Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reaction Using Desorption Electrospray Ionization in High-Throughput and in Leidenfrost Droplet Experiments. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2019, 30, 2144-2151.
[25] H. Zhang#, Z. Wei#, J. Jiang, R. G. Cooks*. Nebulization Prior to Isolation, Ionization, and Dissociation of the Neutral Serine Octamer Allows Its Characterization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 17141-17145.
[26] Z. Wei, X. Zhang, J. Wang, S. Zhang, X. Zhang, R. G. Cooks*. High yield accelerated reactions in nonvolatile microthin films: chemical derivatization for analysis of single-cell intracellular fluid. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7779-7786.
[27] Z. Wei, M. Wleklinski, C. Ferreira, R. G. Cooks*. Reaction Acceleration in Thin Films with Continuous Product Deposition for Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9386-9390.
[28] Y. Zhao, Z. Wei, H. Zhao, J. Jia, Z. Chen, S. Zhang, Z. Ouyang, X. Ma, X. Zhang*. In Situ Ion-Transmission Mass Spectrometry for Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10805-10810.
[29] Y. Zhao, X. Gong, X. Si, Z. Wei, C. Yang, S. Zhang*, X. Zhang*. Coupling a solid phase microextraction (SPME) probe with ambient MS for rapid enrichment and detection of phosphopeptides in biological samples. Analyst. 2015, 140, 2599-2602.
[30] Z. Wei, X. Xiong, C. Guo, X. Si, Y. Zhao, M. He, C. Yang, W. Xu, F. Tang, X. Fang, S. Zhang, X. Zhang*. Pulsed Direct Current Electrospray: Enabling Systematic Analysis of Small Volume Sample by Boosting Sample Economy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11242-11248.
[31] Y. Li, X. Ma, Z. Wei, X. Gong, C. Yang, S. Zhang, X. Zhang*. Pyroelectricity Assisted Infrared-Laser Desorption Ionization (PAI-LDI) for Atmospheric Pressure Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1266-1273.
[32] Z. Wei, S. Han, X. Gong, Y. Zhao, C. Yang, S. Zhang, X. Zhang*. Rapid Removal of Matrices from Small-Volume Samples by Step-Voltage Nanoelectrospray. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11025-11028.
[33] X. Ma, Z. Wei, X. Xiong, Y. Jiang, J. He, S. Zhang, X. Fang, X. Zhang*. Gas-phase fragmentation of host-guest complexes between β-cyclodextrin and small molecules. Talanta. 2012, 93, 252-256.