张顺平
![]()
开通时间:..
最后更新时间:..
研究方向为纳腔光物理。当前开展研究课题:(1)纳腔中光与物质的相互作用规律,包括光子自旋-轨道耦合效应,等离激元-激子强耦合,等离激元与声子等准粒子的相互作用,超灵敏传感;(2)超高带宽片上集成纳米光电信息器件,包括基于隧穿的纳腔电致发光、等离激元电光调制;(3)非线性纳米光子学,基于等离激元与非线性材料混合的二倍频、和频与五波混频等。
Current projects: (1) Light-matter interaction in nanocavities, including photonic spin-orbit coupling in nanocavities, strong coupling of plasmon with excitons, phonons etc., (2) Broadband integrated optoelectronic devices, including light emission via quantum tunneling, plasmonic electro-optic modulator etc. (3) Nonlinear nanophotonics, SHG, SFG and 5WM in plasmonic-photonic hybrid system.
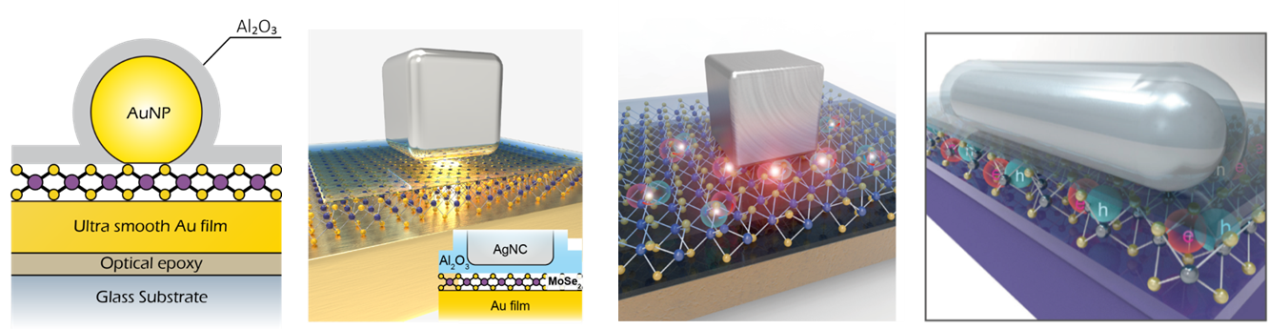
■ Quantum plasmonics. Quantitatively measuring the quantum-limit of plasmonic field enhancement nanocavity [1], achieving record high sensitivity distance sensing using quantum plasmon [2]. Related publications:
[1] Chen, W.; Zhang, S.*; Kang, M.; Liu, W.; Ou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Xu, H.* Probing the limits of plasmonic enhancement using a two-dimensional atomic crystal probe. Light: Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 56.
[2] Chen, W.†; Zhang, S.†; Deng, Q.; Xu, H.* Probing of sub-picometer vertical differential resolutions using cavity plasmons. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 801.
[3] Xu, Y.; Ji, J.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ding, T.; Mao, L.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Quantum plasmonics in nanocavities and its application. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68 (31), 4086-4102. (Invited Review)
[4] Lu, Z.; Ji, J.; Ye, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Quantifying the Ultimate Limit of Plasmonic near-Field Enhancement. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8803.
■ Photonic spin-orbit coupling, optical chirality and helicity. He and collaborators raise the concept of chiral surface plasmon polaritons [1], realized the routing of chiral Raman signal based on spin-momentum locking effect [2] and discover transverse spin-orbit coupling in curve waveguides [7]. Related publications:
[1] Zhang, S.; Wei, H.; Bao, K.; Håkanson, U.; Halas, N.; Nordlander, P.; Xu, H., Chiral Surface Plasmon Polaritons on Metallic Nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107 (9), 096801.
[2] Guo, Q.; Fu, T.; Tang, J.; Pan, D.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Routing a Chiral Raman Signal Based on Spin-Orbit Interaction of Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 183903.
[3] Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Jiang, W.; Shi, J.; Halas, N. J.; Nordlander, P.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Duplicating Plasmonic Hotspots by Matched Nanoantenna Pairs for Remote Nanogap Enhanced Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3499-3505.
[4] Sun, J.; Hu, H.; Pan, D.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Selectively Depopulating Valley-Polarized Excitons in Monolayer MoS2 by Local Chirality in Single Plasmonic Nanocavity. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4953-4959.
[5] Fu, T.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Nanocavity Mediated Directional Coupler in Plasmonics Waveguides. Opt. Commun. 2021, 497, 127160.
[6] Wang, S.*; Liu, X.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Chen, J.; Fu, W.; Sofer, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.*; Zheng, G.* Chiral Au Nanorods: Synthesis, Chirality Origin, and Applications. ACS Nano 2022, 16 (12), 19789-19809.
[7] Fu, T.; Lin, J.; Xu, Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Transverse Spin–Orbit Interaction of Light. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 10783-10789.
■ Strong light-matter interaction in a nanocavity. Achieving strong or intermediate plasmon-exciton coupling using individual metal nanoparticle and monolayer TMDs [1-2], probing the ultrafast decay lifetime in nanocavity [3], explaining different channels process different spectral Rabi splitting [9]. Related publications:
[1] Zheng, D.; Zhang, S.*; Deng, Q.; Kang, M.; Nordlander, P.; Xu, H.* Manipulating coherent plasmon-exciton interaction in a single silver nanorod on monolayer WSe2. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 3809-3814.
[2] Sun, J.†; Hu, H.†; Zheng, D.; Zhang, D.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Light-emitting plexciton: Exploiting plasmon–exciton interaction in the intermediate coupling regime. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10393-10402.
[3] Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Fu, T.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Simultaneous Surface-Enhanced Resonant Raman and Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Monolayer MoSe2: Determination of Ultrafast Decay Rates in Nanometer Dimension. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6284-6291.
[4] Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Understanding the Lineshape of Surface Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectra. National Science Review 2021, Vol. 8, nwab033. (2020.09.23) 2021.04.
[5] Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Strong Plasmon-Exciton Coupling in Transition Metal Dichalcogenides and Plasmonic Nanostructures. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 4408-4419.
[6] Hu, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H. Unified Treatment of Scattering, Absorption, and Luminescence Spectra from a Plasmon–Exciton Hybrid by Temporal Coupled-Mode Theory. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2021, 155, 074104.
[7] Quanbing Guo, Binjie Wu, Rongguang Du, Jiamin Ji, Ke Wu, Yang Li, Zhifeng Shi, Shunping Zhang*, and Hongxing Xu*. Boosting exciton transport in WSe2 by engineering its photonic substrate. ACS Photonics 2022, 9(8), 2817–2824.
[8] Yuhao Xu, Huatian Hu, Wen Chen, Pengfei Suo, Yuan Zhang*, Shunping Zhang*, and Hongxing Xu*. Phononic Cavity Optomechanics of Atomically-thin Crystal in Plasmonic Nanocavity. ACS Nano 2022, 16(8), 12711–12719.
[9] Du, R.; Hu, H.; Fu, T.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H. How to Obtain the Correct Rabi Splitting in a Subwavelength Interacting System. Nano Lett. 2023, 23 (2), 444-450.
■ Nonlinear nanophotonics
[1] Li, Y.; Kang, M.; Shi, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Transversely divergent second harmonic generation by surface plasmon polaritons on single metallic nanowires. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7803-7808.
[2] Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, M.; He, X.; Halas, N. J.; Nordlander, P.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Efficient second harmonic generation in a hybrid plasmonic waveguide by mode interactions. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3838-3845.
[3] Shi, J.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Steering Second-Harmonic Beams in Nanophotonic Waveguides by Gratings. ACS Photonics 2019, 6, 3142-3149.
[4] Guo, Q.; Ou, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Wu, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Efficient Frequency Mixing of Guided Surface Waves by Atomically Thin Nonlinear Crystals. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7956-7963.
[5] Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H. Extraordinary Five-Wave Mixing in a Zinc Oxide Microwire on a Au Film. Nano Lett. 2023, 23 (15), 6966-6972.
[6] Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.*; Xu, H.* Coherent Second Harmonic Generation Enhanced by Coherent Plasmon–Exciton Coupling in Plasmonic Nanocavities. ACS Photonics 2023, 10 (5), 1529-1537.
[7] Zhang, T.; Cui, K.; et al. Nano Lett. 2025 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c04595